Guest WiFi + abuse control for beginners
From DD-WRT Wiki
|
English • Deutsch • Español • Français • Italiano • 日本語 • Polski • Português • Русский • Svenska • 中文(中国大陆) • 中文(台灣) • |
Wiki Path: DD-WRT Wiki Main / Tutorials / Guest Network / Guest WiFi + abuse control for beginners
- Also see Multiple WLANs
Contents |
Introduction
This tutorial provides the basics to create a "guest" wireless Virtual Access Point (VAP) to provide Internet access, but prevent private network access to guest users.
Before proceeding, ensure the router has functional wireless and Internet access, with a working reset button. Backup the router configuration (Administration >> Backup tab in the DD-WRT Control Panel) in case of issues.
Note: very old Broadcom SoC's may be incapable of multiple simultaneous SSIDs, so check the chip revision (corerev):
- 0-4 does not support multiple SSIDs (regardless of unique identifiers)
- 5-8 supports multiple SSIDs (but not with unique identifiers)
- 9+ supports multiple SSIDs (with unique identifiers)
Reference: howtogeek.com
Instructions
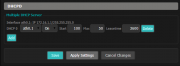
Go to Wireless->Basic Settings in the DD-WRT Control Panel and click "Add" in the "Virtual Interfaces" section. A new Virtual Interface is created, with a title like:
- Virtual Interfaces wl0.1 SSID [dd-wrt_vap] HWAddr [22:AA:4B:36:EC:10]
Note the string after "Virtual Interfaces" (e.g. "wl0.1" is from a Broadcom device) to help identify the correct section of later Control Panel pages to apply settings.
Change the Wireless Network Name (SSID) from the default "dd-wrt_vap" to how you want it to appear to guest users when they connect to your network, e.g., "MyNetwork_guest".
Enable AP isolation so guest users cannot see each other. AP Isolation drops all traffic between clients connected to the VAP. This is recommended to prevent wireless snooping attacks via the guest Wi-Fi. Click on the Save button at the bottom of the page otherwise these settings will be lost when switching tabs.
Go to Wireless->Wireless Security to set the security type and wireless network password. Although the VAP can function with no encryption and password, it can lead to abuse and is thus not recommended. Click Save again.
Set Network Configuration to Unbridged, Enable NAT (gives guests Internet access), and enable Net Isolation (creates firewall rules blocking guests from the private network). Net isolation only works on an unbridged interface with newer builds, starting from build: 23020 (Broadcom), 24759 (Atheros), 25934 (MediaTek/Ralink)
- AP Isolation = Guests cannot see each other on guest VAP
- Net isolation = Guests cannot see your private LAN+WLAN
Enable Forced DNS Redirection and enter the OpenDNS server IP (208.67.222.222) in the Optional DNS target field. This will prevent users from using their own DNS servers (and hence get around content filtering) by intercepting DNS queries and forcing them to use the DNS servers you specify.
Enter the IP Address and Subnet Mask e.g. 172.16.1.1 / 255.255.255.0 (see Private Networks). Click Apply for the new interface to be created e.g. wl0.1. This VAP will now be visible in a wireless scan, but DHCP is required for clients to connect.
Go to Setup >> Networking in the DHCPd section and Add a DHCP server for the new guest network then choose the VLAN (e.g. ath0.1) from drop down menu. Select starting and max number of IP address, plus lease time. Click Apply and wait about 30sec and connecting to Guest Wi-Fi. If not working, power cycle the router. The Internet should be accessible but not the private network nor other clients on network discovery.
Note: There is a newer method using DNSmasq versus DHCPd.
Quality of Service (QoS)
Bandwidth limiting puts the private network on "Maximum" and guest network to "Bulk". The Bulk class is only allocated the remaining bandwidth when other classes are idle. If the pipe is full of traffic from other classes, Bulk will only be allocated 1% of total set limit. This is so your guests will not affect your private network speed. Alternatively, you can manually set hard-coded limits.
Interface limiting, both bridged and unbridged, offers ability to rate-limit or priority-limit services or port(s) ranges. This can be exceptionally useful to control bandwidth hogs, regulate hotspots, etc. with an interface limit, preventing guest users from circumventing QoS limits by changing IP and/or MAC addresses. Abusive users can't bypass your rules without switching off the interface.
Example:
vlan1 512/512 0 ssl manual
This means all traffic on the vlan1 interface (lan ports for some routers, others use eth) is not limited nor shaped, and goes "up to" global limits, except SSL traffic, being limited to 512 kbps (64 kB/s) both up and down. Multiple entries are also possible, for example:
ath0 512/512 0 ssl manual ath0 2048/512 0 http manual ath0 512/512 0 ftp manual
The same applies to what was said above, just for the ath0 wireless interface and only the listed services are rate-limited. Priority limits can also be used, but simultaneous rate limiting and prioritizing on the same service is not supported.
Access Restrictions
Access Restrictions can be used to block torrents and some VPNs. A determined user is very hard to block, because now there are free SSTP VPN services, etc. Cheap consumer routers may not be able to run Proxy, Squid, etc., so to accomplish network abuse filtering OpenDNS can be used.
Wikipedia has a comparison of public DNS resolver services including protocol support and filtering capabilities.
OpenDNS
OpenDNS is a free DNS (Domain Name Server) service to make Internet browsing safer and allegedly faster. By using the OpenDNS DNS server instead of the ISP's DNS server, you are automatically protected from their list of phishing Web sites. However, in order to restrict certain content, e.g., "adult" sites, you will need to create a free account, register your IP address, and select the categories you want restricted — sexuality, nudity, pornography, lingerie, grotesque, etc. Since most of us have DHCP assigned WAN IP addresses that change periodically, we need to instruct our router to tell OpenDNS the new IP address when it changes. See the DNS-O-Matic section of the OpenDNS article. Reboot router, clear browser cache, and manually set public DNS server in your PC NIC adapter to try to avoid restrictions.